California’s earthquake early-warning system is getting a seismic improve, one that may enable residents to obtain extra well timed alerts about shaking from an incoming megaquake.
The improve, additionally out there in Oregon and Washington, will present options vital for warnings in regards to the “Massive One.”
The enhancements may imply that, relying on the place they’re and the place the quake begins, Californians would obtain an earlier, extra correct estimate of magnitude earlier than the earth begins shaking — say from a magnitude 7.8 earthquake that begins on the San Andreas fault close to the Mexican border and ruptures the fault towards Los Angeles County.
The improve additionally would enhance warnings for the Pacific Northwest and California’s North Coast, that are threatened by tsunamis from quakes alongside the Cascadia subduction zone.
The U.S. Geological Survey and its nonprofit companion EarthScope introduced the upgraded system Wednesday.
For essentially the most highly effective earthquakes, the enhancements “develop into very, very vital in serving to us get to the reply faster — when it comes to how large that occasion is,” mentioned Robert de Groot, one of many operations workforce leaders of the USGS’ ShakeAlert System.
For smaller earthquakes, the older system labored “completely tremendous,” De Groot mentioned. However with bigger quakes, the magnitude could possibly be underestimated for fairly a while, robbing residents of essential info within the seconds earlier than they really feel essentially the most damaging shaking.
Let’s say an earthquake on the southern San Andreas fault that begins close to the Mexican border finally ends up being a magnitude 8, however the earliest estimate says it’s a magnitude 6.5. The longer that underestimate is broadcasting to telephones, the much less possible individuals are to take acceptable motion.
“Folks would react in another way — a lot in another way — than should you mentioned it was a magnitude 8,” mentioned David Mencin, vice chairman of knowledge providers for EarthScope, a nonprofit funded by the Nationwide Science Basis, USGS and NASA that’s supplying information for the improved early-warning system.
“The most important, most damaging earthquakes are those that we’re actually apprehensive about,” Mencin mentioned. “This fixes the issue of underestimating these magnitudes, which is vital.”
Probably the most well-known underestimations got here in 2011 with the epic magnitude 9.1 earthquake that triggered a devastating tsunami off the japanese coast of Japan, leaving roughly 18,000 lifeless. An preliminary estimate put the quake’s magnitude at 7.9, that means the precise earthquake was an astonishing 63 instances stronger when it comes to power launched.
That underestimation led to a misjudgment of tsunami heights — with a number of the first detailed alerts erroneously estimating the tsunami could be decrease than protecting sea partitions. And when communications have been lower off, a false sense of safety settled in, with many individuals by no means receiving correct evacuation alerts.
Had Japan used GPS information, a extra correct magnitude of the quake may’ve been generated way more shortly, Mencin mentioned.
The USGS’ West Coast earthquake early-warning system has lengthy relied on a whole bunch of seismic sensors embedded within the floor. However there may be solely a lot shaking they will detect in a short while.
“Seismometers are likely to get overwhelmed for earthquakes which might be magnitude 7 and higher. They’ll start to get ‘saturated,’” Mencin mentioned. Throughout notably intense shaking, the seismometers — mainly objects on a spring — begin to hit the wall of the instrument, and so the seismic sign is “clipped” and may’t shortly calculate magnitudes above a sure threshold.
Coming to the rescue now are a whole bunch of GPS sensors on Earth’s floor and run by EarthScope. More often than not, these sensors observe very sluggish motion, on the order of millimeters or much less per 12 months. That may illustrate delicate tectonic plate motion between main earthquakes, illustrating how the Pacific plate, the place L.A. is situated, is nudging northwest relative to the North American plate, the place the Mojave Desert is situated.
However in a serious earthquake, there may be appreciable, everlasting motion of the bottom, the place one piece of land jolts away from the opposite, shifting yards in seconds. Within the nice San Francisco earthquake of 1906, land on one facet of the San Andreas fault usually jammed 8.5 toes previous the opposite, De Groot mentioned.
And within the final nice southern San Andreas earthquake — rupturing the fault in 1857 between Monterey and San Bernardino counties — land on one facet of the fault usually lurched 10 toes relative to the opposite facet. Each the 1857 and 1906 earthquakes have been someplace round magnitude 7.8.
Within the largest of the Ridgecrest earthquakes in 2019, there have been about 2 toes of fault offset for the magnitude 7.1 quake, De Groot mentioned.
The primary calculation of the earthquake early-warning system will nonetheless depend on seismic sensors, which measure floor velocity and acceleration, De Groot mentioned. Then, as a quake continues to rupture alongside a fault, GPS sensors will measure the gap a block of land has moved.
“What GPS permits us to do is to get a deal with on how large that earthquake is getting — or could possibly be — sooner,” De Groot mentioned. Which means the early-warning system may understand a quake was a magnitude 7, or greater, a couple of seconds sooner than earlier than.
It’s vital to know that an earthquake’s magnitude doesn’t seem immediately. Quakes rupture on a fault on the velocity of sound via rock, which is slower than the sunshine velocity of in the present day’s telecommunications methods. That is the precept that permits individuals farther away from the beginning of an earthquake to get seconds of advance warning of the worst shaking to return.
On the San Andreas fault, an earthquake that begins rupturing on the Salton Sea and ends at Mt. San Gorgonio, roughly 80 miles away, would produce a magnitude 7.3 earthquake.
A rupture of the San Andreas fault between the Salton Sea and Mt. San Gorgonio may produce a magnitude 7.3 quake.
(Angelica Quintero / Los Angeles Occasions)
However one which ruptures all the 340-mile size of the southern San Andreas, ending in Monterey County, would create a magnitude 8.2 earthquake and produce shaking over a a lot wider swath of Southern and Central California.
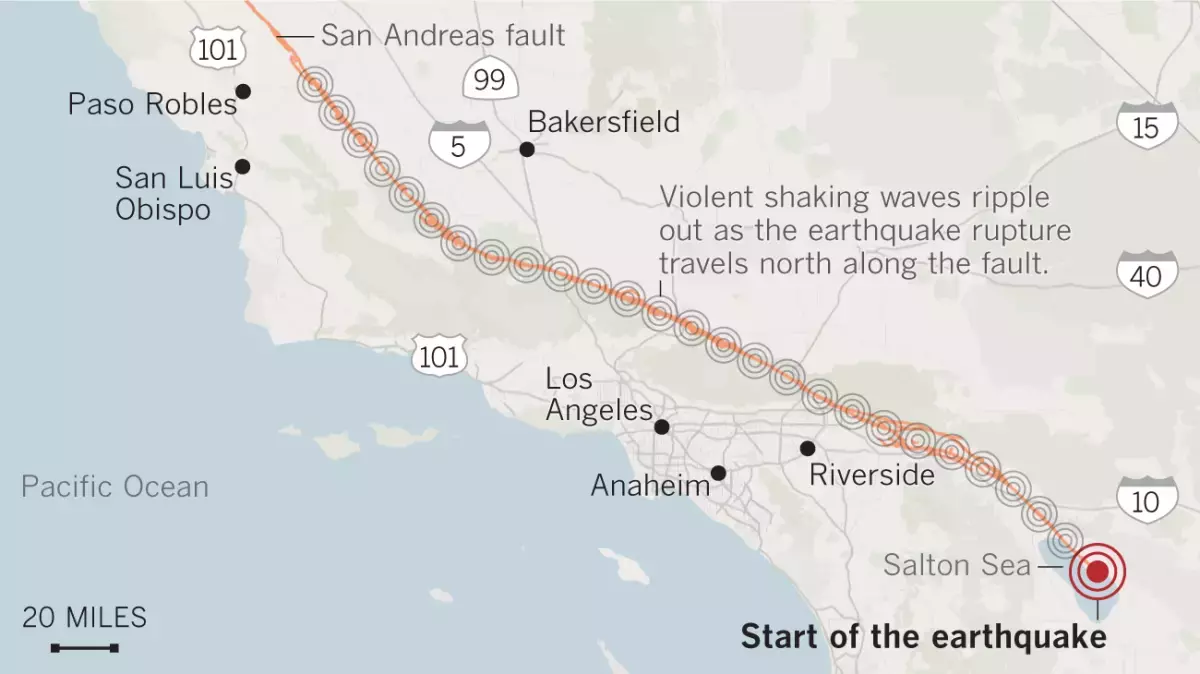
A rupture of all the 340-mile size of the southern San Andreas fault between Monterey County and the Salton Sea would produce a magnitude 8.2 earthquake.
(Angelica Quintero / Los Angeles Occasions)
“Because the earthquake grows in measurement, it’ll have the ability to assist replace that magnitude extra shortly and with extra accuracy,” De Groot mentioned of the GPS information, which can unfold the early warnings to a bigger area. “By including within the [GPS] information, you truly get a deal with on how large the earthquake actually is sooner.”
The web outcome will “translate into longer warning instances for individuals who may probably get alerts on their telephones,” De Groot mentioned. That may give individuals extra time to take motion, corresponding to surgeons and dentists shifting sharp instruments from close to sufferers, permitting trains to sluggish to cut back the danger of derailment, opening firehouse doorways earlier than they are often jammed shut and giving the general public time to drop, cowl and maintain on.
Relying on the place individuals are, some might not get a warning earlier than they really feel the primary shaking, which is called the “P wave.” However the purpose is to present a warning earlier than essentially the most damaging shaking happens — the “S wave” — which comes later.
“What we actually wish to get individuals to learn about is getting the alert earlier than the strongest shaking,” De Groot mentioned.
By the top of 2025, the USGS’ ShakeAlert — which is about 90% full — is anticipated to have 1,675 seismic sensing stations. EarthScope says a further 1,000 GPS stations run by the nonprofit are contributing information to the system.
EarthScope, the nation’s major seismological and geodetic information facility, was lately fashioned because the merger of UNAVCO, which held an archive for GPS information, and IRIS, which held a seismic information archive.
The earthquake early-warning system has develop into extra widespread lately as individuals get extra accustomed to the alerts. In February’s extensively felt magnitude-4.6 earthquake in Malibu, some felt unnoticed once they didn’t obtain an early warning.
The alerts could be obtained by downloading the free MyShake app on iOS and Android. Android customers are routinely subscribed to Android Earthquake Alerts. These methods are set to sound an alarm when an earthquake is estimated to be of magnitude 4.5 or greater and the anticipated shaking depth on the person’s cellphone location is anticipated to be not less than “weak” — degree 3 on the Modified Mercalli Depth Scale, the place it’s felt fairly noticeably by individuals indoors and should rock standing motor autos barely or really feel like a truck is passing by.
Earthquakes of higher power — magnitude 5 and above — will ship customers a wi-fi emergency alert, much like an Amber Alert, in the event that they’re in a location anticipated to get not less than “mild” shaking depth. That’s degree 4 on the Modified Mercalli Depth Scale — shaking depth sufficient to rattle dishes, home windows and doorways, and may really feel like a heavy truck hanging a constructing.













